Stage-1 (2025)
As part of Activity Act.1.1. (WP1) of the POLHSYS project, seven hydrophobic fibrous materials based on PVDF-HFP copolymer and various fillers (CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite, graphite, and nanoclay) were prepared using the electrospinning method. The electrospun materials (Fig.1) obtained were characterized by advanced instrumental analysis techniques: SEM, EDAX, VSM, FTIR, and mechanical tests. The porosities and water contact angles were also determined. The oily liquids (hydrophobic pollutants) used in the sorption tests were characterized for density, viscosity, and surface tension. The sorption capacities of the electrospun materials for collecting oily liquids were evaluated.
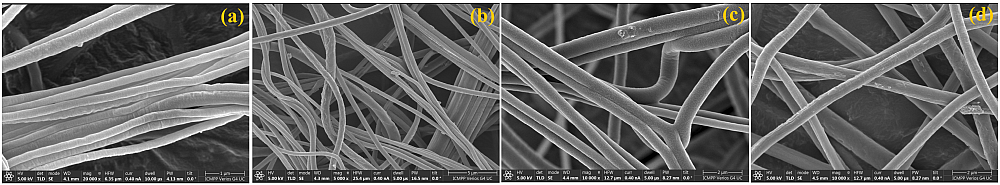
Fig. 1. SEM micrographs of fibrous membranes produced by the electrospinning technique: (a) PVDF-HFP, (b) PVDF-HFP/CoFe2O4, (c) PVDF-HFP/CoFe2O4/graphite, (d) PVDF-HFP/CoFe2O4/ nanoclay.
Within the framework of Activity Act.1.2. (WP2), three porous membranes based on polyetherimide (PEId, main polymer), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP, porogen), and kaolin-type nano-clay (filler) were obtained by the phase-inversion method. The membranes were characterized in terms of mechanical properties, IR spectra, water contact angle, porosity, and water permeation tests. Activity Act.1.3 (WP3) involved the synthesis, morphological and structural characterization, and testing of nanostructured inorganic photocatalysts based on cerium-doped zinc oxide (ZnO:Ce) and dysprosium-doped titanium oxide (TiO2:Dy). Herein, the effect of dopant concentration and sintering temperature on the photodegradation efficiency of recalcitrant organic pollutants was investigated. Supporting activity Act.1.4 (WP4) involved nonlinear regression modeling of the kinetic curves of photodegradation of organic pollutants and the determination of rate constants. For the TiO2:Dy/Ciprofloxacin system, the optimal operating conditions were established through design of experiments (DoE) and a statistical modeling approach relying on the response surface methodology. |








