EXECUTION STAGE 1/2022
Development of metal oxide nanoparticles, fluorescent organic precursors and of the corresponding polyurethanes
The activities proposed for the first stage of the project were:
1.1. Synthesis and functionalization of metal oxide nanoparticles (TiO2, ZnO, MnO2)
1.2. Preparation of fluorescent monomers (diols of coumarin, dansyl or pyrene) to be used in polyurethane synthesis
1.3. Design and synthesis of new polyurethane elastomers bearing fluorescent sequences
All the proposed activities were addressed and completed, the main results being summarized as follows:
In accordance with the proposed objectives, the first approached activity consisted in the synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles, the studies carried out at this stage aiming the design and preparation of new zinc oxide nanoparticles. Although ZnO nanoparticles have a wide band gap energy (Eg = 3.37 eV), their major advantage compared to other photocatalysts is that they absorb a larger fraction of the UV spectrum. However, the wide band gap of the ZnO semiconductor results in low photocatalytic efficiency in the UV region due to the rapid recombination of photogenerated electron-hole pairs, which is why preventing the recombination of electron-hole pairs by reducing the band gap of ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) improves the photocatalytic performance. Therefore, a series of zinc oxide nanoparticles was synthesized, using various preparative conditions, their characterization being carried out by specific methods (FTIR spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, EDX spectroscopy). In addition, the estimation of the band gap energy values shows that these varied for the synthesized ZnO NPs between 3.14 and 3.21 eV, and after functionalization with a silane-type derivative, the Eg value decreases to 2.97 eV.
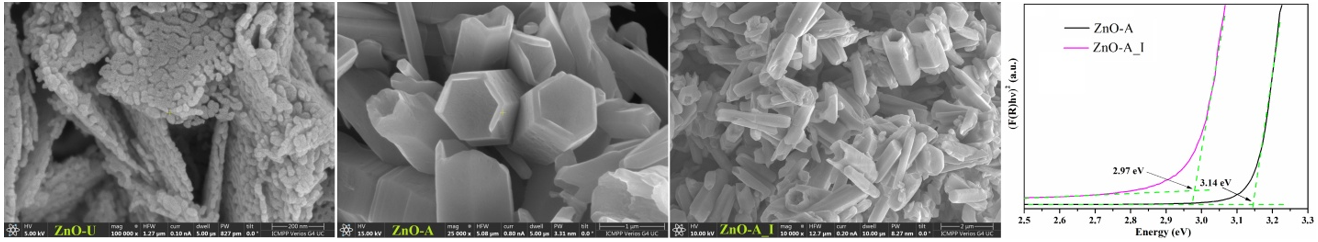
The organic functionalization of ZnO nanoparticles with silane-type units and iodide ions was proposed as a convenient method of linking the inorganic units to the polyurethane chain through quaternization reactions, aiming a better dispersion of the nanoparticles in the organic matrix and preventing their migration during the photocatalytic activity testing.
In order to introduce fluorescent sequences into the polyurethanes chains, the synthesis and characterization (1H NMR, 13C NMR, FTIR, UV-Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy) of two types of diols bearing fluorescent units derived from coumarin was carried out, and the monomer with the best optical characteristics has been used in various ratios in the preparation of fluorescent polyurethane elastomers. The synthesized polyurethanes were also spectrally characterized to confirm the structure and to evaluate the optic characteristics, subsequent studies being directed towards the preparation of fluorescent polyurethane/ZnO nanoparticle hybrid nanocomposites and the testing of their photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation.
EXECUTION STAGE 2/2023
Development of metal oxide nanoparticles, fluorescent organic precursors and of the corresponding polyurethanes
The activities proposed for this stage of the project were:
2.1. Synthesis and functionalization of metal oxide nanoparticles (TiO2, ZnO, MnO2) (objective 1.1.)
2.2. Preparation of fluorescent monomers (diols of coumarin, dansyl or pyrene) to be used in polyurethane synthesis (objective 1.2.)
2.3. Design and synthesis of new polyurethane elastomers bearing fluorescent sequences (objective 2.)
2.4. Development of hybrid materials through covalent attachment of functionalized metal oxide nanoparticles to polyurethane chains (objective 3.)
2.5. Thoroughly characterization of the fabricated nanocomposites. Evaluation of the photocatalytic abilities of the proposed materials (objective 4.).
All the proposed activities were addressed and completed, the main results being summarized as follows:
In this stage, the series of metal oxide nanoparticle was diversified with the design and preparation of new titanium and manganese dioxide nanoparticles, special attention being paid to the shape and size of the nanoparticles as well as to the band gap energy variation. 9 types of TiO2 nanopowders and 3 types of manganese oxide nanoparticles were prepared, which differ from each other by their crystalline structure, lattice parameters, size and morphology of the final particles, etc., aspects that were evaluated with the help of specific characterization techniques. Further, some selected TiO2, MnO2 and ZnO (synthesized in stage I) nanoparticles were functionalized with silane units and chloride ions (using 3-chloropropyl trimethoxysilane derivative) through a sol-gel reaction in order to immobilize them by quaternization in the polyurethane chain. The band gap energy values (Eg) for inorganic NPs varied between 3.00 and 3.16 eV (3.16 eV for ZnO, 3.15 eV for TiO2 and 3.00 eV for MnO2) and after the functionalization with a silane-type derivative, Eg decreased to 2.95 eV for ZnO-Si, 2.83 eV for TiO2-Si and 2.54 eV for MnO2-Si.
Also, during this stage, fluorescent diols with dansyl or pyrene units were synthesized, the proposed structures being characterized by spectral methods (1H NMR, 13C NMR, FTIR, UV-vis, PL). Then, a series of polyurethane elastomers with dansyl-type fluorescent units was obtained, the ratio of dansyl diol used in the synthesis of polyurethanes being of 0.5 mol % and 1.0 mol %, respectively.
To generate hybrid materials, the ZnO NPs synthesized in the previous stage, functionalized with 3-iodopropyl trimethoxysilane, were attached by quaternization to the tertiary nitrogen atoms in the structure of polyurethanes with coumarin units (also reported in stage I). The prepared samples include various molar percents of coumarin chromophore (1 mol %, 5 mol % and 10 mol %, respectively) and two different types of silanized ZnO NPs (nanosheets or nanorods).
Investigation of the optical properties for the polyurethane/ZnO NPs hybrid films with or without coumarin-type fluorophore was carried out by UV-Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy, the band gap energy (Eg) of the hybrid films being calculated from their reflectance spectra using the Kubelka-Munk method. Based on the Eg values, all the synthesized samples (A_0 – 10 and B_0 – 10) were tested as photocatalysts under visible light irradiation, using malachite green (MG) as a model pollutant.
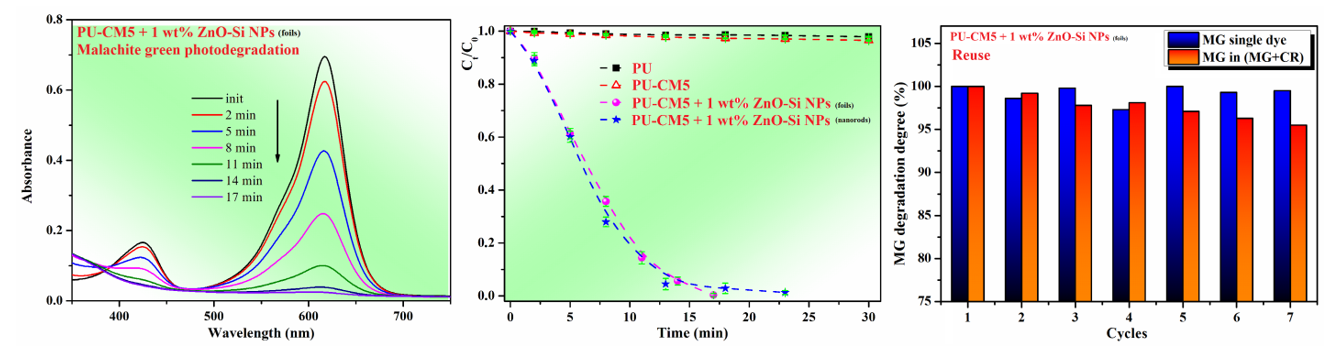
Malachite green photodecomposition takes place in the presence of all hybrid materials containing ZnO NPs, the time required for the complete removal of MG varies between 18 and 100 min, depending on the sample used. The absence of ZnO NPs from PU films does not activate MG photodegradation, and the adsorption effect of polyurethane films can be ignored. Also, the reusability and stability of the hybrid catalyst films were tested, the removal efficiency of MG as a single pollutant in aqueous solution varied between 97.3 % and 100 %, and for MG as a component of the mixture with Congo Red (MG-CR) varied between 95.5 % and 100 %, after 7 successive catalysis cycles.
EXECUTION STAGE 3/2024
Development and optimization of hybrid materials based on fluorescent polyurethanes and functionalized metal oxide nanoparticles
The activities proposed for this stage of the project were:
3.1. Design and synthesis of new polyurethane elastomers bearing fluorescent sequences (objective 2)
3.2. Development of hybrid materials through covalent attachment of functionalized metal oxide nanoparticles to polyurethane chains (objective 3)
3.3. Thoroughly characterization of the fabricated nanocomposites. Evaluation of the photocatalytic abilities of the proposed materials (objective 4).
All the proposed activities were addressed and completed, the main results being summarized as follows:
The structural and compositional diversity of polyurethanes, which modulates the final characteristics of thermoplastic polyurethanes, is very easy to achieve by conveniently selecting the constituent units intended to lead to the obtaining of materials with a wide spectrum of physical characteristics and also allows the incorporation of suitable functional groups that offer numerous application opportunities. Therefore, in this stage of the project, polyurethane elastomers with dansyl and pyrene fluorescent monomers, taken in various molar ratios were prepared and the structurally characterized by spectral methods (FTIR, 1H NMR). The optical properties of polyurethanes with or without fluorescent dansyl and pyrene units, investigated using UV-Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy, indicate an increase in the intensity of the absorption maxima with increasing chromophore percentage, while the fluorescence quantification indicates a higher influence on the emission bands exerted by the aggregation of fluorescent units in solution and the occurrence of the self-quenching phenomenon, or by the solvent polarity (observed especially for pyrene molecules).
To generate hybrid materials, in this stage we have included the metal oxides functionalized with 3-chloropropyl trimethoxysilane in different ratios (1 wt. %, 3 wt % or 5 wt. %), in the polyurethane elastomers with dansyl and pyrene photosensitizers. The prepared composites were characterized by different methods (ATR-FTIR, UV-Vis, fluorescence), to evaluate the optical and structural characteristics. Also, for the hybrid films, the mechanical properties were tested by recording the stress-strain curves, observing an improvement in the tensile strength of the films, given by the presence of inorganic nanoparticles, at the expense of deterioration in elasticity. Likewise, the evaluation of the hydrolytic and enzymatic stability at pH = 7 and 37 °C for 30 days did not reveal a significant decrease in weight of the samples, indicating a good resistance in aqueous environment for polyurethane-based composites.
The photocatalytic efficiency of composite films prepared using polyurethanes with dansyl-type chromophore and functionalized inorganic nanoparticles was tested in the photodegradation of rhodamine B, a possible persistent carcinogenic pollutant, frequently found in contaminated waters, while the photocatalytic activity of nanocomposites based on polyurethane elastomers with pyrene and zinc oxide functionalized nanoparticles was evaluated in the decomposition of the organic dye methylene blue, under visible light irradiation.
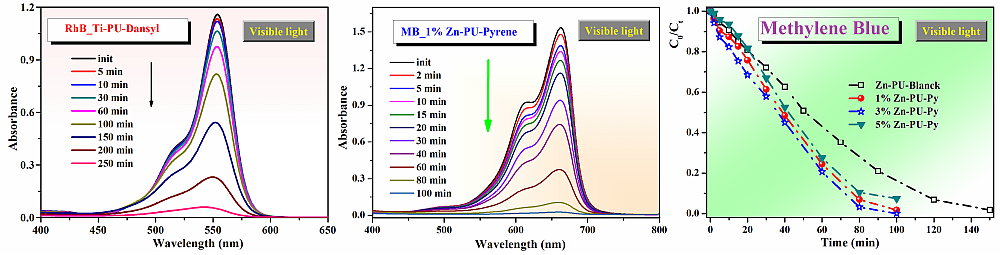
The obtained results demonstrate that for the tested films, the pollutants are almost completely degraded under visible irradiation. By comparing the photocatalytic activity of the samples with and without chromophore, it was observed a lower photocatalytic activity for the film without chromophore, highlighting the contribution of the photosensitized in the photodegradation process. In contrast, a variation in the amount of inorganic nanoparticles does not bring significant differences in the photodegradation rate of MB, so for economic reasons, it is recommended to use a reduced amount of inorganic component.
In order to elucidate the mechanism of action of the hybrid films, which contain within the same macromolecule ZnO nanoparticles as photocatalytic units and the coumarin chromophore as photosensitizer for inorganic entities, a series of tests were performed in the presence of various scavengers. The objective was to capture free radicals (superoxide species, holes or hydroxyl species) formed in the degradation process of the pollutant dye using p-benzoquinone (p-BQ), glycerol (Gly) and tert-butyl alcohol (t-BuOH) as scavengers. The results of the tests indicated that the superior photocatalytic efficiency of the hybrid film can be attributed to the generation of a greater number of electron/hole pairs and to the improved charge separation caused by the coumarin photosensitizer present in the polyurethane composition. | 





