
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
OBJECTIVES 2014:
1. Synthesis and electro-optical characteristics of aromatic oligoazomethine/permethylated α-cyclodextrin main-chain polyrotaxanes (OA-Rot and its non-rotaxane OA counterpart
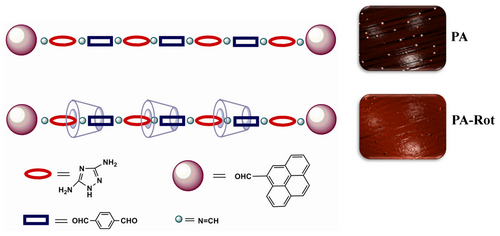
Figure 1 Chemical structures of OA and OA-Rot oligoazomethines
2. Poly[2,7-(9,9-dioctylfluorene)-alt-(5,5'-bithiophene)] main-chain polyrotaxanes
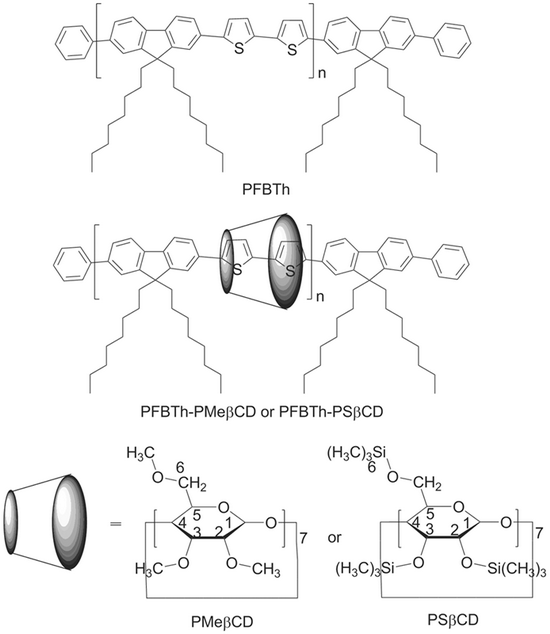
Figure 2.The chemical structures of the investigated compounds: PF-BTh, PF-BTh•PMeβCD and BTh•PSβCD
3. Molecular wire formation from poly[2,7-(9,9-dioctylfluorene)-alt-(5,5-bithiophene/cucurbit[7]uril)] polyrotaxane copolymer
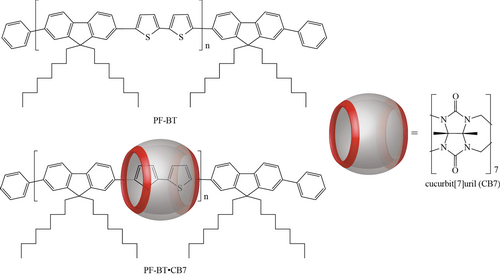
Figure 3. The chemical structures of the reference PF-BT and molecular wire PF-BT•CB7
3.1. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Studies
The 2D AFM images with scan lengths of 5 µm and 1.5 µm of copolymers and their cross-section profiles of spin-coated thin films on mica substrates are shown in Figure 4.
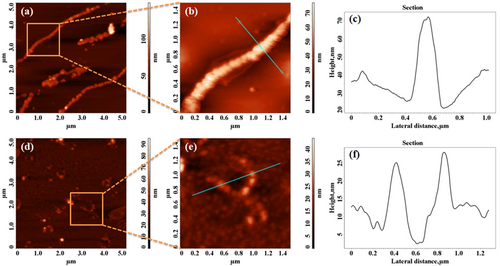
Figure 4. The 2D AFM topography images with scan lengths of 5 and 1.5 µm of: PF-BT•CB7 (a, b), PF-BT (d, e) and their cross-section profiles (c, f)
4. Polyfluorenes encapsulated into permodified cyclodextrin derivatives
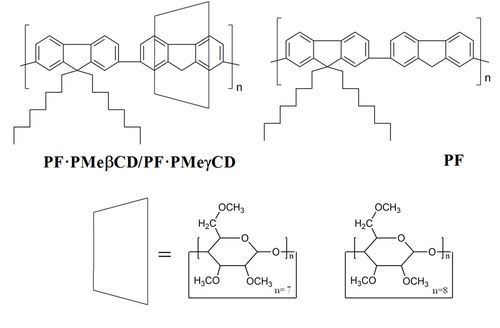
Figure 5. The chemical structures of the polyrotaxanes PF·PMeβCD and PF·PMeγCD and its non-rotaxane PF counterpart
5. Synthesis, electro-optical and morphological properties of randomly distributed electron-donor and rotaxane electron-acceptor with permodified cyclodextrins units into 9,9-dioctylfluorene chains
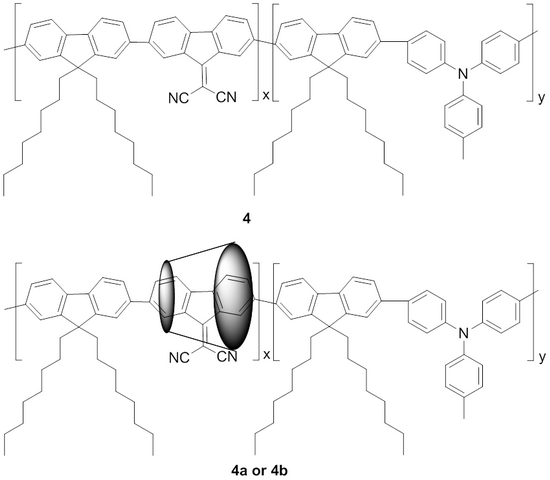
Figure 6. Chemical structures of the non-rotaxane 4, 4a and 4b polyrotaxane copolymers

